Investigation walkthrough for an issue related to multiple classloaders available when SpringBoot application is deployed on IBM WebSphere Liberty (WSL).
Motivation
Recently I was investigating a strange issue that was present only in a production-like environment. Fortunately, my team have CI which is almost 1 to 1 with production so we were able to catch this issue before deployment. So what’s different between production and local environment you may ask. Well, the answer is very simple - we use different servlet containers. For local development, we use embedded Tomcat web server that is ship together with SpringBoot. On production, we have WSL application server. Because I wanted to know why the issue was happening only on one environment and working perfectly fine on another I had to dig a little bit.
Context
Before moving forward with the analyze let’s give some context so that what I will write next will have more sense. As always it starts with a simple task in Jira backlog. The task was to move complex authorization mechanism from service to web layer.
authorization is the process of verifying that “you are permitted to do what you are trying to do”
source: Wikipedia
The difference on performing authorization on these two layers is that services operate on actual objects where web controllers on identifiers of these objects. Below is pseudo code for the change that was planed.
Before:
aspect(object) {
return allowedToAccess(object)
}After:
aspect(identifier) {
const object = resolveObjectFrom(identifier)
return allowedToAccess(object)
}For now, we know what needs to be done and how. But one more important addition to the context is about convention* we try to follow in our code base - which is - extensive usage of encapsulation which in our case is more about creating a clear interface for others who will be using these objects than just hiding information.
* clarification - we follow more conventions/best practices but in the context of this post, only this single convention is important.
But what this exactly mean? In simple words, we use public modifier only when it’s really required, if not then we operate mostly using only private and package protected modifiers. I think the above context should be enough to start analyzing a concrete example. To make analyze simpler I have created a sample application demonstrate a problem and can be found on github.
Analyze
Posotive scenario
For our case, we need to focus only on three elements.
HelloControlerthis is standardRestControllerto which one dependency is injected.
@RestController
class HelloController {
private final HelloService helloService;
HelloController(HelloService helloService) {
this.helloService = helloService;
}
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}")
ResponseEntity<String> hello(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(helloService.sayHello(name));
}
}PointcutedHelloControlleris special becausePointcutedHelloController#hellois join point for around advice (AOP terminology)
@RestController
class PointcutedHelloController {
private final HelloService helloService;
PointcutedHelloController(HelloService helloService) {
this.helloService = helloService;
}
@GetMapping("/hello-aop/{name}")
ResponseEntity<String> hello(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(helloService.sayHello(name));
}
}LoggingAspectwhich registers advice around specified pointcut
@Aspect
@Component
class LoggingAspect {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggingAspect.class);
@Around("within(com.example.demo.PointcutedHelloController)")
Object aroud(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
LOG.info(pjp.getSignature().toLongString());
return pjp.proceed();
}
}You can run tests or application itself (mvn spring-boot:run) and call hello methods - everything will work as expected. Please notice, if you will place breakpoint in PointcutedHelloController#hello you will see that PointcutedHelloController is wrapped with com.example.demo.PointcutedHelloController$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB proxy.
Negative scenario
First you will have to change profile setting activeByDefault from false to true in pom.xml so it looks like this:
<id>wlp</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>then you just need to build war package (mvn clean package -DskipTest) and deploy it to WSL. After starting the server it crashes with the following message:
Caused by: org.springframework.aop.framework.AopConfigException: Could not generate CGLIB subclass of class com.example.demo.PointcutedHelloController: Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class; nested exception is org.springframework.cglib.core.CodeGenerationException: java.lang.IllegalAccessError-->class com.example.demo.PointcutedHelloController$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$4f0e109d cannot access its superclass com.example.demo.PointcutedHelloController
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy.getProxy(CglibAopProxy.java:208) ~[spring-aop-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory.getProxy(ProxyFactory.java:110) ~[spring-aop-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator.createProxy(AbstractAutoProxyCreator.java:471) ~[spring-aop-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator.wrapIfNecessary(AbstractAutoProxyCreator.java:350) ~[spring-aop-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization(AbstractAutoProxyCreator.java:299) ~[spring-aop-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:429) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1782) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:593) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
... 32 common frames omitted
Caused by: org.springframework.cglib.core.CodeGenerationException: java.lang.IllegalAccessError-->class com.example.demo.PointcutedHelloController$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$4f0e109d cannot access its superclass com.example.demo.PointcutedHelloController
at org.springframework.cglib.core.ReflectUtils.defineClass(ReflectUtils.java:530) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cglib.core.AbstractClassGenerator.generate(AbstractClassGenerator.java:363) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer.generate(Enhancer.java:582) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cglib.core.AbstractClassGenerator$ClassLoaderData$3.apply(AbstractClassGenerator.java:110) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cglib.core.AbstractClassGenerator$ClassLoaderData$3.apply(AbstractClassGenerator.java:108) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cglib.core.internal.LoadingCache$2.call(LoadingCache.java:54) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run$$$capture(FutureTask.java:266) [na:1.8.0_201]
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java) [na:1.8.0_201]
at org.springframework.cglib.core.internal.LoadingCache.createEntry(LoadingCache.java:61) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cglib.core.internal.LoadingCache.get(LoadingCache.java:34) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cglib.core.AbstractClassGenerator$ClassLoaderData.get(AbstractClassGenerator.java:134) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cglib.core.AbstractClassGenerator.create(AbstractClassGenerator.java:319) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer.createHelper(Enhancer.java:569) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer.createClass(Enhancer.java:416) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ObjenesisCglibAopProxy.createProxyClassAndInstance(ObjenesisCglibAopProxy.java:57) ~[spring-aop-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy.getProxy(CglibAopProxy.java:205) ~[spring-aop-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
... 39 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalAccessError: class com.example.demo.PointcutedHelloController$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$4f0e109d cannot access its superclass com.example.demo.PointcutedHelloController
at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass1(Native Method) ~[na:1.8.0_201]
at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass(ClassLoader.java:763) ~[na:1.8.0_201]
at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor27.invoke(Unknown Source) ~[na:na]
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) ~[na:1.8.0_201]
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498) ~[na:1.8.0_201]
at org.springframework.cglib.core.ReflectUtils.defineClass(ReflectUtils.java:527) ~[spring-core-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
... 54 common frames omittedFirst thing that caught my attention was Could not generate CGLIB subclass of ...: Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class which seems to be fair enough as controller class is not public so it can be non-visible but then next question arises - why this was working locally when deployed on Tomcat? At this point removing AOP advice from PointcutedHelloController#hello metod, fix the problem. This clearly indicates that there is something wrong when using Spring AOP. Maybe it requires classes and method to be public? Let’s see what documentation says about it. Most important fragment of this documentation to my current situation is:
With CGLIB, public and protected method calls on the proxy are intercepted (and even package-visible methods, if necessary).
And this is true when deploying on Tomcat but not when on WSL. Because I’m not a WSL expert I had to do some googling to find out that this issue can be related to classloaders. Where one classloader is used to load all 3rd party libraries from /WEB-INF/lib and my own classes from /WEB-INF/classes and another when creating proxy for PointcutedHelloController.
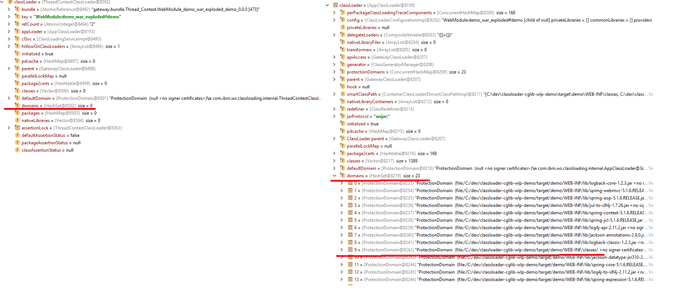
After debugging session I was able to nail down which classloader is used when creating proxy.
Spring AOP creates its proxies through CglibAopProxy#getProxy(classLoader). This ClassLoader object in the end is provided by DefaultResourceLoader which sets classLoader to Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader() during object construction. Bellow is screenshot which shows how classLoader provided by DefaultResourceLoader (left) differs from classLoader awaible in any other place of my application when calling getClass().getClassLoader()
It looks like the one created by DefaultResourceLoader is not aware of my classes so that’s the reason why application crashes on startup.
Fix
We know that everything starts in DefaultResourceLoader so we can register our custom ServletContextInitializer to override default classLoader created by DefaultResourceLoader. This can be done by extending SpringBootServletInitializer class like so:
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder applicationBuilder) {
return applicationBuilder.sources(DemoApplication.class)
.initializers(configurableApplicationContext -> {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader();
((DefaultResourceLoader)configurableApplicationContext).setClassLoader(classLoader);
});
}
}It is possible becouse configurableApplicationContext is instance of AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext class which in turn is subclass of DefaultResourceLoader.